Our guideways and housings work together to solve countless engineering challenges across numerous industries and applications. Therefore, sizing and selecting an assembly or linear guide system should be a careful and systematic process.
Choosing the right linear motion supplier and product can be a difficult process. Incorporating incorrectly sized or poor quality components will compromise the performance of the OEM product. Machine motion will be slower and less accurate, resulting in lower production yields, incorrect component placement, and potential end-product damage. Machine downtime and failures will become more frequent. Slide life will be shortened, and maintenance costs will rise.
1. Check Static, Dynamic, and Moment Load Capacities
The first thing to consider is the loads that will be applied to your linear guide system. Will the guideway only carry static loads, or will it also need to carry dynamic loads when in motion? Manufacturers will list the maximum static and dynamic load capacities for that particular linear guideway to make selection easier. Static load refers to the static load that occurs when the linear component is fixed or stationary. Static load ratings are always higher than dynamic load ratings. You need to choose the type of guideway based on your needs.
Linear Guideways manufacturers will also list moment load ratings, and these must also be carefully considered. If the linear guides and rails are likely to experience moment loads, a dual rail setup can minimize rolling moment loads by distributing the forces to one or two linear guides on each rail. The life of the linear system will be greatly extended by using a dual rail configuration and therefore eliminating any moment loads.
2. Layout and installation considerations
Having considered static and dynamic load capacities, the next consideration should be the layout of the linear system. A single rail with one linear guide may be sufficient, but as mentioned previously, if there are over-suspended moment loads, using a dual rail setup (with one or more linear guides per rail) may eliminate these moment loads by distributing the loads across two rails.
Ensuring that the prepared surface is suitable for mounting the linear guides is critical and should be carefully considered. The surface should be flat, clean, and when using a dual rail setup, the rails should be checked for alignment after installation. Installation instructions for all linear guides can be found via the datasheet.
3. Consider speed and acceleration requirements
Critical speed should be the next consideration in selecting a linear guide. How fast you need your linear system to run will narrow your selection. Typically, profiled linear guides have a maximum allowable speed of 3-5m/s and an acceleration of 300m/s2.
4. What accuracy class is required for the application
Once the load, speed and layout are specified, it is critical to ensure that your linear system is repeatable to achieve the desired end result. Linear guide manufacturers display the accuracy class as the running parallelism over a defined guide length, and the deviation over a set length in microns. The accuracy class is then defined as N, H, P, SP and UP. By using these tables and matching the class to the requirements of the machine, the correct linear guide selection can be made.
5. Travel Length (Stroke)
A simple but critical step in linear guide selection. Calculate the total travel length required, remembering to account for the “lost” travel from the length of the linear guide. If the total travel needs to be more than 4000mm, a butt joint is required to achieve a smooth joint where the two linear guides join. NSAR can provide a perfectly finished end to the butt joint, allowing for smooth, quiet linear motion throughout the entire travel.
6. Linear Guide Selection and Environmental Conditions
It is critical to consider the conditions in which the linear guide system will operate. If the environmental conditions are likely to be harsh, it is important to ensure that the correct seals and scrapers are selected to ensure a long service life. We has a market-leading range of seals and scrapers that protect against contaminants such as dust and chips.
Linear guides are widely used in various industries such as robotics, laboratory equipment, machine tools, 3D printing, etc. NSAR produces innovative, market-leading linear solutions.
7. Consider the impact of materials and coatings on cost and lead time
When specifying bearings, people tend to focus on mechanical parameters, while materials and coatings are considered less important. In fact, materials and coatings can have a significant impact on the project, not only from a performance perspective, but also from a cost and lead time perspective. For example, anti-corrosion options may include everything from thin and dense chrome plating to various black chrome platings. In some cases, choosing a stainless steel version of the linear guide may provide a more effective solution.
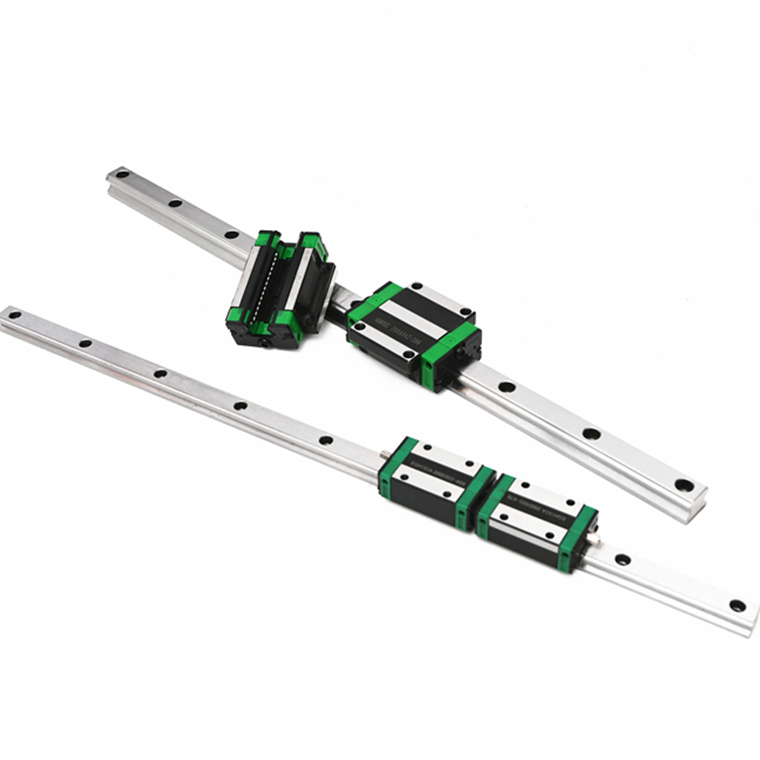

8. Choose the best linear guide for you
In summary, the choice of linear guide is critical to achieving the best performance of your linear motion system.
Whether you choose profile, flat, round or square guides, smart choices ensure seamless, easy mechanical operation. Click to view NSAR matching bearing products.
9. Customize products for competitive advantage
More than 50% of linear motion products are custom made. Why? Because OEMs want to build products that offer a unique competitive advantage. This goal requires components to be lighter, smaller and able to handle greater forces, speeds and loads. It may require modified cages, special coatings or corrosion-resistant materials.
Copyright © NSAR Bearings. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy